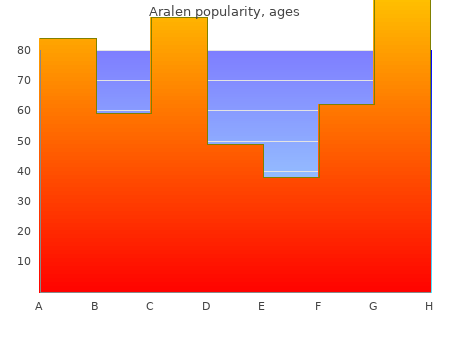
By W. Sinikar. Rochester College.
This con- trasts with younger pain patients 250mg aralen with amex, who endorse their own behaviors and ac- tions as a strongest determinant of pain severity discount aralen 250 mg. In agreement with previ- ous studies (see Melding, 1995, for review), a belief in chance factors was also shown to be associated with increased pain, depression, functional im- pact, and choice of maladaptive coping strategies. Finally, using a newly de- veloped psychometric measure of pain attitudes, Yong, Gibson, Horne, and Helme (2001) found that older persons living in the community exhibited a greater belief in the need for stoic reticence and an increased cautious re- luctance and self-doubt when making a report of pain. These findings are in agreement with early psychophysical studies that show that older persons adopt a more stringent response criterion for the threshold report of pain and are less willing to label a sensation as painful (Clark & Mehl, 1971; Harkins & Chapman, 1976, 1977). The finding is also consistent with other recent studies of stoic attitudes in older pain patients (Klinger & Spaulding, 1998; Machin & Williams, 1998; Morley, Doyle, & Beese, 2000) and provides strong empirical support for the widely held view that older cohorts are generally more stoic in response to pain. Another potentially important psychological influence relates to possi- ble age differences in self-efficacy and the use of pain coping strategies. Self- efficacy in being able to use coping strategies to effectively reduce the se- verity of pain does not appear to change between early adulthood and older age (Corran et al. These findings would seem to challenge the commonly held view that older persons have less self-efficacy and instead show a stability and resilience in beliefs of personal competence across the major portion of the adult life span. Studies by Keefe and colleagues (1990, 1991) showed no age differences in the fre- quency of coping strategy use, although there was a strong trend for older adults to use more praying and hoping than their younger counterparts. PAIN OVER THE LIFE SPAN 133 Conversely, older people with chronic pain have been found to report fewer cognitive coping strategies and an increased use of physical methods of pain control when compared to young adults (Sorkin et al. Consistent with others (Gardner, Garland, Workman, & Mendelson, 2001; Mosley et al. Such differences are thought to be more likely due to sociocultural cohort effects rather than to some maturational change per se (Corran et al. The use of catastrophizing as a cognitive cop- ing strategy was found to be the strongest predictor of negative clinical presentation in both young and older adults (accounting for 20–30% of the variation in outcome scores). This finding is consistent with many earlier studies in young adult chronic pain patients (see Jensen, Turner, Romano, & Karoly, 1991, for review) and has since been confirmed in older popula- tions as well (Bishop, Ferraro, & Borowiak, 2001). It is in the use of other coping strategies, however, that age differences start to emerge. In the elderly cohort, self-coping statements and diverting attention were shown to be significant predictors of clinical outcome measures, whereas ignoring pain and reinterpretation of pain sensations were of more importance in young chronic pain patients.
That is aralen 500mg with visa, provide them with one or more concrete strategies or goals (eg 500mg aralen with visa, 5 minutes per day of stretching exercises, simple relax- POTENTIAL BIASES ON THE PART OF ation techniques, leaving the house at least once a HEALTH CARE PROVIDERS day) to pursue on their own. How well do and disability levels of their patients, and this bias is you listen when they speak? How much input do your strongest when the patients are elderly or are mem- patients have regarding treatment decisions? For example, among back pain patients followed longitudinally, no relationship was observed REFERENCES between providers’ estimates of patients’ rehabilita- tion potential and actual rehabilitation outcomes. Pain catastrophizing reports of pain are exaggerated or feigned, no and kinesophobia: Predictors of chronic low back pain. Pain and emotion: produce higher scores on measures of pain, distress, New research directions. Psychological factors in chronic pain: scores with acceptable sensitivity and specificity have Evolution and revolution. Chronic pain sec- The prevalence of opioid abuse and dependence ondary to disability: A review. Pain self-efficacy beliefs and RECOMMENDATIONS FOR HEALTH pain behaviour: A prospective study. Changes in beliefs, catastrophizing, and coping are associated with improve- Develop standardized assessments of psychosocial ment in multidisciplinary pain treatment. J Consult Clin factors, such as mood, coping, and social relation- Psychol. Biopsychosocial approaches to the chosocial factors should include an interview, behav- treatment of chronic pain.
The ability to assess an athletes’ The medical plan purchase aralen 500 mg overnight delivery, chain of command and level of care blood glucose and sodium levels will assist with their provided must be reviewed with the medical staff cheap aralen 250 mg with mastercard. It is rapid evaluation and allow for the appropriate treat- helpful although not always practical to provide an ment of a collapsed athlete (Davis, et al, 2001). COMMUNICATION PLAN COMPETITORS It is vital that medical support assets have the ability to communicate with each other, EMS assets, local Participants should also be given medical informa- hospitals, and the event director before, during, and tion prior to the event. Additions to event web- include cellular phones, computer networks, ham radio, sites, handouts to accompany the race packet pick-up 22 SECTION 1 GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS IN SPORTS MEDICINE and information posters displayed in common areas are important in the evaluation, treatment, and disposi- are several examples. Fortunately most and health warnings has been used with success at complaints are nonsevere in nature and can be quickly numerous events (Cianca et al, 2001). These can be quickly differentiated from nonsevere conditions by MEDICAL AND NONMEDICAL SUPPORT the evaluation of mental status, rectal temperature (Roberts, 2000), blood pressure, and pulse. Serum glu- The appropriate staffing of medical treatment areas cose and sodium levels may also aid in the diagnosis. The some of these severe conditions may be treated at the composition and number of this staff will vary medical aid station or transported via EMS to the most depending on the location and nature of the event. MUSCULOSKELETAL College of Sports Medicine (Armstrong et al, 1996) is to provide the following medical personnel per 1000 run- Medical conditions, such as exercise associated col- ners: 1 or 2 physicians, 4–6 podiatrists, 1–4 emergency lapse, heat stroke, chest pain and hyponatremia can be medical technicians, 2–4 nurses, 3–6 physical thera- triaged from muscle cramps, blisters, and extremity pists, 3–6 athletic trainers, and 1–3 assistants. Approximately 75% of these personnel should be sta- This separation of care allows the assignment and tioned at the finish area. This also allows injured athletes, documentation, medical tracking, those with more severe conditions to be treated in the and provide information within the medical aid station same area where they can be more closely moni- and to event staff. This area is reserved for athletes who are waiting for transporta- After the event it is most important to elicit feedback tion for nonsevere conditions or who are not prepared from both medical and nonmedical staff. This often to leave the medical area, but do not require further identifies areas that had not been considered in the ini- care. This group is continuously observed and encour- tial planning and execution phases of the event.